D-Fructose
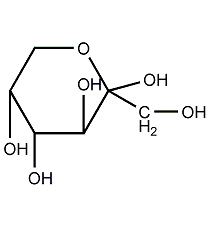
Structural formula
| Business number | 018P |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C6H12O6 |
| Molecular weight | 180.16 |
| label |
Fructose; D-levulose; D-arabinohexose, Fruit sugar, D-Levulos, sweetener |
Numbering system
CAS number:57-48-7
MDL number:MFCD00148910
EINECS number:200-333-3
RTECS number:LS7120000
BRN number:1239004
PubChem ID:None
Physical property data
1. Properties: white rhombic prism crystals or crystalline powder. It exists in both furanose and pyranose forms. Sugar has the sweetest taste. Very easy to deliquesce.
2. Density (g/mL, 25/4℃): 1.60
3. Relative vapor density (g/mL, air=1): Undetermined
4. Melting point (ºC): 103~105℃ (decomposition)
5. Crystal phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -2810.4
6. Crystal phase standard claimed heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -1265.6
7. Refractive index: Undetermined
8. Flash point (ºC): Undetermined
9. Specific rotation (º): [α]D20 -132°→-92° (C=2)
10. Autoignition point or ignition temperature (ºC): Undetermined
11. Vapor pressure (kPa, 25ºC): Undetermined
12. Saturated vapor Pressure (kPa, 60ºC): Undetermined
13. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol): Undetermined
14. Critical temperature (ºC): Undetermined
15. Critical pressure (KPa): Undetermined
16. Log value of oil-water (octanol/water) partition coefficient: Undetermined
17. Explosion upper limit (%, V/V): Undetermined
18. Lower explosion limit (%, V/V): Undetermined
19. Solubility: Easily soluble in water, hot acetone, 1g product Soluble in 15ml ethanol, 14ml methanol, soluble in pyridine, ethylamine and methylamine, slightly soluble in cold acetone.
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity: rabbit intravenous LD50: 15mg/kg 2. Other multiple dose toxicity: rat oral TDLo: 119mg/kg/14D-I
Ecological data
None
Molecular structure data
5. Molecular property data:
1. Molar refractive index: 37.15
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 102.4
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K): 317.1
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm)���91.8
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 14.73
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for calculation of hydrophobic parameters (XlogP): -3.2
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 5
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 6
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 5
5. Number of tautomers: 6
6. Topological molecular polar surface area (TPSA): 118
7. Number of heavy atoms: 12
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 147
10. Isotopes Number of atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 3
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine chemical bonds Number of stereocenters: 0
14. Number of stereocenters of uncertain chemical bonds: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
None
Storage method
This product should be sealed and stored in a cool, dry place.
Synthesis method
1. Industrial large-scale production uses starch hydrolysis to produce glucose, which is converted into invert sugar by immobilized glucose isomerase, which contains 42% fructose and 58% glucose. After its separation, fructose is obtained.
Purpose
1. For biochemical and microbiological research. Determination of boric acid.
2.Fructose can directly supply heat energy, replenish body fluids and nourish the whole body, and is easier to absorb and utilize than glucose. In addition to being used as medicine, it is also used in high-end candies and beverages. Used as a sweetener in gargles.
extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/1070extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/dabco-xd-102-catalyst-cas106317-60-3-evonik-germany/extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/45037extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/dioctyltin-oxide-doto/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/67874-71-9/extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/category/products/page/108extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/category/products/page/167extended-reading:https://www.morpholine.org/category/morpholine/n-acetylmorpholine/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/nt-cat-la-300-catalyst-cas10861-07-1-newtopchem/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/-T120-1185-81-5-didodecylthio-dibutyltin.pdf


