sucrose
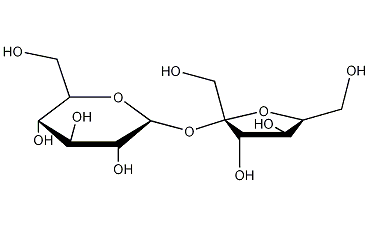
Structural formula
| Business number | 018Q |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C12H22O11 |
| Molecular weight | 342.3 |
| label |
α-D-Glc-(1→2)-β-D-Fru, D(+)-Saccharose,Sucrose, Sugar, Saccharose, beet sugar, granulated sugar; white granulated sugar; soft white sugar, β-D-Fructofuranosyl-α-D-glucopyranoside, α-D-Glucopyranosyl β-D-fructofuranoside, Cane sugar, Genetic engineering research reagents |
Numbering system
CAS number:57-50-1
MDL number:MFCD00006626
EINECS number:200-334-9
RTECS number:WN6500000
BRN number:90825
PubChem number:24899768
Physical property data
1. Properties: Colorless monoclinic wedge-shaped crystals, white particles or crystalline powder. Sweet and hygroscopic
2. Relative density (g/mL, 25/4℃): 1.587
3. Relative vapor density (g/mL, air=1) : Undetermined
4. Melting point (ºC): 185~187
5. Crystal phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -5640.4
6. Crystal phase standard claims heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -2226.1
7. Refractive index : Undetermined
8. Flash point (ºC): Undetermined
9. Specific rotation (º): Undetermined
10. Autoignition point or Ignition temperature (ºC): Undetermined
11. Vapor pressure (kPa, 25ºC): Undetermined
12. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa, 60ºC): Undetermined
p>
13. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol): Undetermined
14. Critical temperature (ºC): Undetermined
15. Critical pressure (KPa): Undetermined Determined
16. Log value of oil-water (octanol/water) partition coefficient: Undetermined
17. Explosion upper limit (%, V/V): Undetermined
18. Lower explosion limit (%, V/V): Undetermined
19. Solubility: Easily soluble in water, slightly soluble in ethanol, insoluble in organic solvents such as ether and ethyl ester. .
Toxicological data
None
Ecological data
None
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 70.85
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 192.8
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K): 628.7
4. Surface Tension (dyne/cm): 113.0
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 28.09
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): -3.7
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 8
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 11
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 5
5. Number of tautomers:
6. Topological molecular polar surface area (TPSA): 190
7. Number of heavy atoms: 23
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 395
10. Isotopic atoms Quantity: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 9
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine chemical bond positions Number of stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
Stable under normal temperature and pressure.
Storage method
Packaging in food-grade plastic bags and woven bags. Store in a cool and dry place.
Synthesis method
1. A large amount of sucrose comes from cane sugar and beet. Sugar cane contains about 15-20% sucrose, and beet contains 10-17%. There are also different contents in various other fruits, seeds, leaves, flowers, and roots. Squeeze out the liquid from sugar cane or extract sugar juice from sliced beets with water. Use lime clarification method or combined with sulfurous acid filling method to remove impurities in the sugar juice. After filtration, vacuum evaporate the filtrate to thicken, recrystallize and separate to obtain jaggery, and then Refined sugar is obtained through decolorization and recrystallization.
2.Dissolve ordinary sucrose in water, filter, and then evaporate under reduced pressure. Pure product available.
Purpose
1. Sucrose is the most commonly used sweetener. The annual production and consumption of sucrose in the world is about 80 million to 100 million tons. It can also be used as chemical raw materials, such as the synthesis of sucrose lipids, etc.
2. Used for the preparation of analytical reagents and biological nutrients.
3. Sucrose is the most common edible sugar and is also used to make citric acid, caramel, invert sugar, transparent soap, etc. , sucrose can inhibit bacterial growth at high concentrations and is used in medicine as a preservative, antioxidant and tablet excipient.
extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/k-15-catalyst/extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/40376extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/Catalyst-8154-NT-CAT8154-polyurethane-catalyst-8154.pdfextended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/CS90-catalyst–CS90-polyurethane-catalyst-CS90.pdfextended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/benzyldimethylamine/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/amine-catalyst-a-300/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/wp-content/uploads/2016/05/Lupragen-N205-MSDS.pdfextended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/44834extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/lupragen-n106-strong-foaming-catalyst-di-morpholine-diethyl-ether-basf/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/dabco-33-s-addocat-106-teda-l33b/


